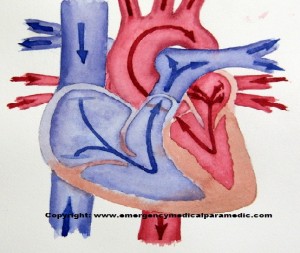
Blood Flow Through The Heart
The following page discusses how blood flows through the human heart. The human heart is basically a very economical pump, designed to last you a lifetime. The heart itself can be broken into 4 main chambers, the right and left atrium and the right and left ventricles, which are designed to pump blood around the body. The right atrium and ventricle are two interconnected chambers that pump separately to the left atrium and ventricle, which are also interconnected chambers.
Here is an image of the blood flow through the heart:
1. Deoxgyenated blood, which is blood that has already released most of its oxygen to the cells to maintain homeostasis, enters the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava. From here, it enters the right atrium and flows into the right ventricle, through the contraction of the right atrium. 2. The right ventricle then pumps the deoxgynated blood into the pulmonary trunk. 3. From the pulmonary trunk, the deoxygenated blood travels up the pulmonary trunk, which divies into the right and left pulmonary arteries and then pulmonary capillaries (this is where the deoxgynated blood picks up oxygen in the lungs and loses its CO2). 4. Newly oxgyenated blood is now returned to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins and then into into the left ventricle (the larger of the two ventricles). 5. Oxygenated blood is then ejected into the body through the aortic arch and throughout the body.
How Does Blood Flow Through the Heart?
The blood flows through the heart through both pre-load (back-logged blood from the rest of the circulatory system) and through the opening of various valves within the heart and the contraction of the left and right ventricles which cause the blood to be literally pumped around the heart and body.
What is the Purpose of the Heart?
The purpose of the heart is to literally pump oxygenated blood around the body to provide the oxygenation of all cells within the tissues of the body in exchange for CO2.
Return to: ECG Interpretation Tutorial.
Next page in the ECG Interpretation Tutorial: